Segmentation System
- 프로그램을 논리적 block으로 분할 (segment)
ㆍBlock의 크기가 서로 다를 수 있음
- 특징 :
ㆍ메모리를 미리 분할하지 않음. (VPM과 유사)
ㆍSegment sharing / protection이 용이함
ㆍ메모리를 동적으로 분할하기 떄문에, Address mapping 및 메모리 관리의 overhead 가 큼
-> 대신 메모리를 효율적으로 활용할 수 있다.
ㆍNo internal fragmentation
-> External fragmentation 발생 가능
Address Mapping
- Virtual address : v = (s, d)
ㆍs : segment number
ㆍd : displacement in a segment
- Segment Map Table (SMT)
- Address mapping mechanism
ㆍPagin system 과 유사

그림 1은 Segment Map Table을 나타낸 것이다. PMT에서 ([PintOS, Project3] 메모리 관리 1. Paging System (tistory.com) 참조) Segment length랑 protection bit가 추가된 것을 알 수 있다.
- Segment length : Segment 의 길이
- Protection bits (R/W/X/A) : Segment에 대한 접근 권한을 나타낸다.
ㆍR : Read 가능
ㆍW : Write 가능
ㆍX : eXecute 가능
ㆍA : Append 가능
Address Mapping
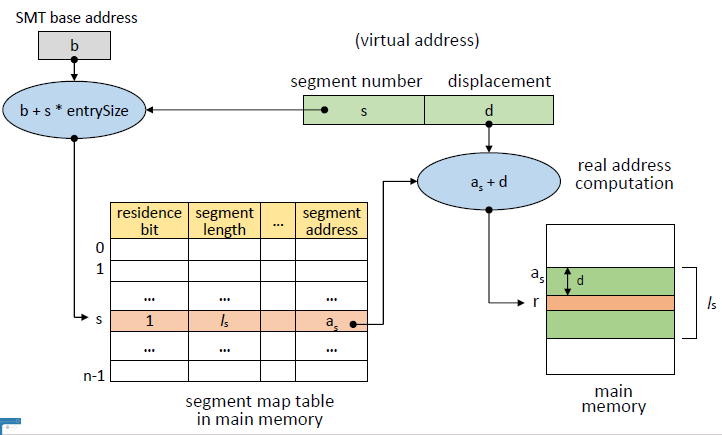
Direct Mapping의 경우 PMT 등과 크게 다르지 않다.
1. 프로세스의 SMT가 저장되어 있는 주소 b로 접근한다.
2. virtual address의 segment number s를 이용하여 b에서의 s엔트리를 찾는다.
- s entry의 위치 = b + s * entrySize
3. 찾은 Entry에 대해 할당되어 있는 주소인지 확인한다.
1) 할당되지 않은 경우 : swap device로부터 해당 segment를 메모리로 적재하여 SMT를 갱신한다.
2) d가 segment 길이보다 큰 경우 (d > l(s)), segment overflow exception 처리 모듈을 호출
3) 허가되지 않은 연산일 경우 (protection bit field 검사), segment protection exception 처리 모듈을 호출
4. 실제 주소 r 계산 ( r = a(s) + d )
5. r로 메모리에 접근
Hybrid Paging / Segmentation
- Paging (고정 크기 분할) 과 Segmentation (논리적 분할) 을 결합
ㆍPage sharing / Protection이 쉽다.
ㆍ메모리 할당 / 관리 overhead가 작다.
ㆍ외부 단편화가 없다.
- 프로그램 분할
ㆍ논리 단위의 segment로 분할
ㆍ각 segment를 고정된 크기의 page들로 분할
ㆍPage 단위로 메모리에 적재
- 전체 테이블 수의 증가
ㆍ메모리 소모가 큼
ㆍAddress mapping 과정이 복잡하다
- Direct mapping의 경우, 메모리 접근이 3배이다.
ㆍ메모리 접근에 시간이 길다.
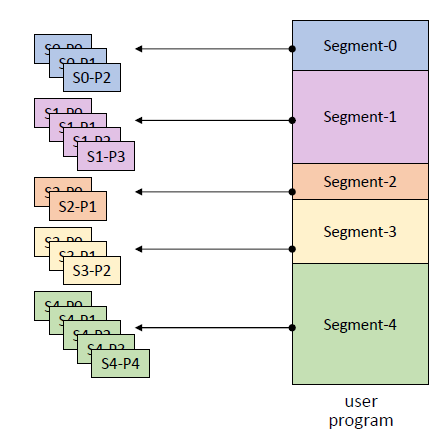
Address Mapping
- Virtual Address : v = (s, p, d)
ㆍs : segment number
ㆍp : page number
ㆍd : offset in a page (displacement)
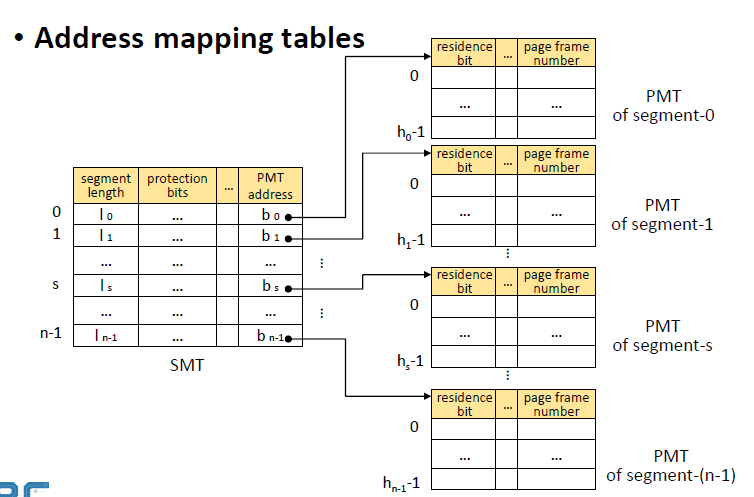
- SMT와 PMT 모두 사용
ㆍ각 프로세스 마다 하나의 SMT
ㆍ각 segment 마다 하나의 PMT
ㆍ실제로 main memory에 올라가는 것은 Page이다.
- Address mapping
ㆍDirect, associated 등
- 메모리 관리
ㆍFPM 과 유사
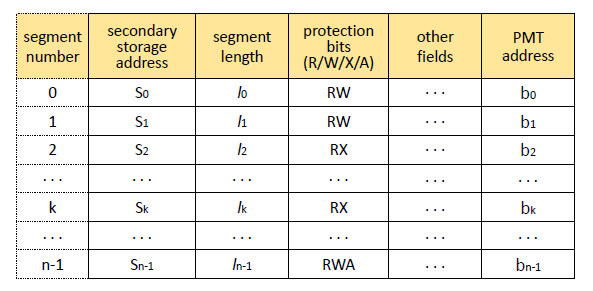
그림 4-1의 SMT에는 residence bit가 있지 않다.
-> Segment에 올라가는 것은 실제 메모리 주소가 아니라 PMT address가 있기 때문이다.
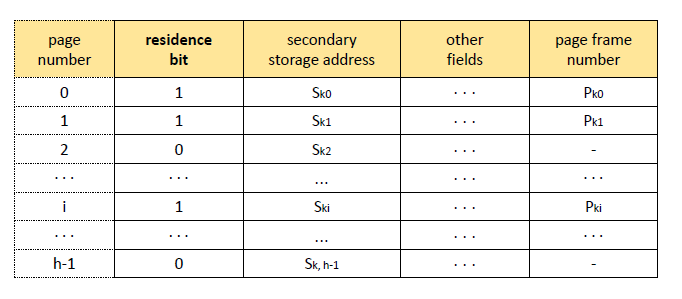
그림 4-2의 PMT에는 residence bit가 있다.
-> Page frame에는 실제 메모리 주소가 있어야하기 때문이다.
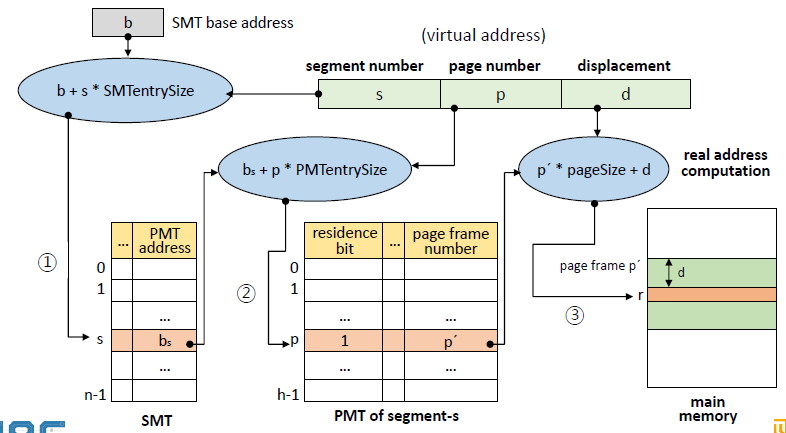
Hybrid System에서 main memory로 접근하는 흐름은 다음과 같다.
1. SMT base address b와 segment number s로 SMT로 접근한다. ( b + s * SMT entrySize )
2. SMT에서 PMT address b(S)를 찾아, page number p를 활용해 page frame number p`를 알아낸다. ( b(s) + p * PMT entrySize )
3. p`와 d를 통해 실제 주소를 가져온다. ( p` * pageSize + d )
'Pintos Project > 이론 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [PintOS, Project 3] Virtual Memory Management - SW Components (0) | 2021.02.18 |
|---|---|
| [PintOS, Project 3] Virtual Memory Management - Cost Model / HW Components (0) | 2021.02.18 |
| [PintOS, Project3] Virtual Memory - Paging System (0) | 2021.02.18 |
| Lecture 5 : Process Scheduling (0) | 2021.01.30 |
| Lecture 4 : 스레드 관리 (Thread Management) (0) | 2021.01.29 |




댓글